20 Implementing complex agents
20.1 Second-tier model: Pond Trade with cultural evolution
We will now go over the implementation of the second-tier Pond Trade model (steps 10-13). The pace in this section will be significantly faster. I would like you to focus only on the main aspects added at each step, and not worry about the files already in the root directory.
Could you remember the conceptual model for this tier that we defined at the beginning?
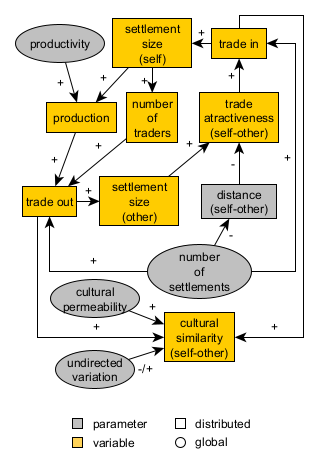
Pond Trade conceptual model at start (second tier)
We will now extend the Pond Trade model to include a simple mechanism of cultural evolution.
First, we will implement a simple model of cultural transmission, integrated with the Pond Trade model. For this, we will use the so-called “vector model” of cultural transmission (Axelrod 1997; Lipo 2017; Shennan 2009; Bentley, Hahn, and Shennan 2004; Battiston et al. 2017).
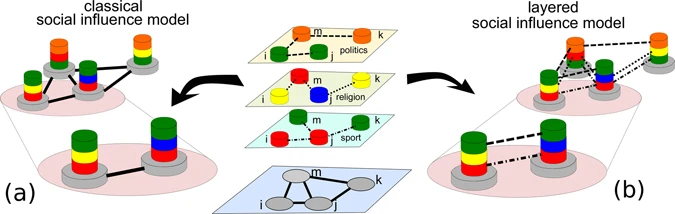
Illustration of the idea of cultural vectors (Battiston et al. 2017, Fig. 1)
Following this model, each settlement has a “cultural vector”, which is a list of cultural traits (e.g., pottery styles, architectural styles, etc.) that represent the aggregated culture of the population of the settlement. These cultural vectors can be modified through the movement of trade goods between settlements, according to a “cultural permeability” that defines how easily cultural traits are transmitted between settlements. In addition, cultural vectors can be modified randomly over time through intrinsic cultural variation (undirected variation) and selection, in which specific cultural traits are more likely to be transmitted or retained based on their “fitness” in the environment.
20.2 Implementing Cultural transmission 🤔
Our goal here will be to implement the following:
- a cultural “vector” of settlements, representing a series of cultural traits of the aggregated population of the settlements
- a mechanism to modify these cultural vectors through the movement of trade goods, according to a global measure of what we call here “cultural permeability”
Before looking at the solution, could you try to write the code yourself?
Things to consider:
- How to represent the cultural vectors?
- How to represent the cultural permeability?
- How do trade goods modify cultural vectors?
- How to visualise the cultural vectors?
Solution (creating cultural vectors):
Let us start with implementing the settlements’ cultural vector (culturalVector). Since there is, for now, no meaning of traits, we can use this new variable to hold the values of the three numbers defining an RGB colour (i.e., red, green, blue; values between 0 and 255) that will then be shown as the icon colour of the settlement.
settlements-own
[
...
culturalVector
]
...
to create-coastal-settlements
; consider only coastal patches
let coastalPatches patches with [(isLand = true) and (any? neighbors with [isLand = false])]
repeat numberOfSettlements
[
; ask a random coastal patch without a settlement already
ask one-of coastalPatches with [not any? settlements-here]
[
sprout-settlements 1 ; creates one "turtle" of breed settlements
[
set sizeLevel 1 ; the size level is initiated at minimum (i.e., 1)
set stock 0
set frequencyOverQuality random-float 1
set culturalVector extract-rgb color
; for now, we represent three continuos cultural traits of settlements
; initialized as the rgb values of the settlement color.
set shape "circle 2"
]
; replace the land path cost with the port pathCost
set pathCost relativePathCostInPort
; exclude this patch from the pool of coastal patches
set coastalPatches other coastalPatches
]
]
end
to update-display
paint-routes
paint-active-routes
; scale the size of settlements according to their dynamic free-scaled sizeLevel
let maxSettlementSize max [sizeLevel] of settlements
ask settlements
[
set hidden? not showSettlements
set size 1 + (sizeLevel / maxSettlementSize) * 9
set color rgb (item 0 culturalVector) (item 1 culturalVector) (item 2 culturalVector)
]
ask traders
[
ifelse (isActivated)
[ set hidden? false ]
[ set hidden? true ]
]
end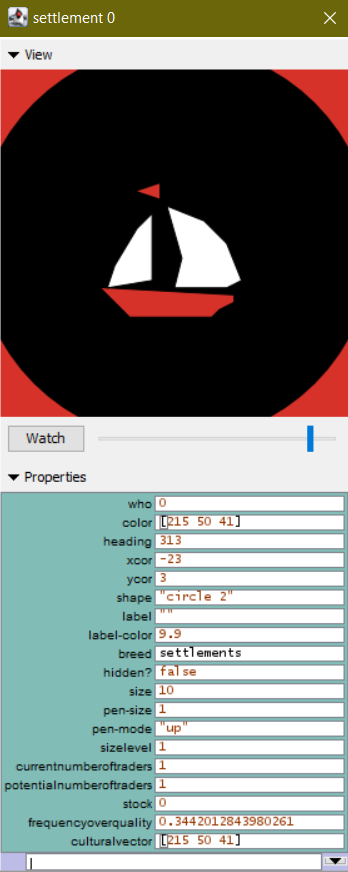
Settlement with cultural vector
Solution (transmission):
Next, we add a mechanism for traders to record the state of their base culturalVector while loading their cargo and to pass this vector as an influence on another settlement’s culturalVector when unloading. More specifically, this influence will decrease the difference between values in each trait to a value determined by the parameter traitTransmissionRate (slider, from 0 to 25, by 0.01, default value = 1).
traders-own
[
...
culturalSample
]
...
to load-cargo ; ego = trader
let settlementHere one-of settlements-here
; load cargo
set cargoValue [stock] of settlementHere
ask settlementHere [ set stock 0 ] ; empty the settlement stock
set culturalSample [culturalVector] of settlementHere
end
...
to add-trade-effect [ aTrader ] ; ego = settlement
; cultural transmission trader to port
let newCulturalVector []
foreach culturalVector
[ ?1 ->
let otherSettlementTrait item (length newCulturalVector) [culturalSample] of aTrader
let traitChange (otherSettlementTrait - ?1) * (traitTransmissionRate / 100)
set newCulturalVector lput (?1 + traitChange) newCulturalVector
]
; print (word "========== " self " ============")
; print (word "old vector: " culturalVector ", new vector: " newCulturalVector)
set culturalVector newCulturalVector
set sizeLevel sizeLevel + [cargoValue] of aTrader
end20.3 Checking the milestone File (step 10)
With these changes, the model dynamics will now include a general cultural convergence whenever trade partners become stable, especially when trade hubs emerge. After a few thousand simulation steps, the visual result is that all settlements hold the same colour.
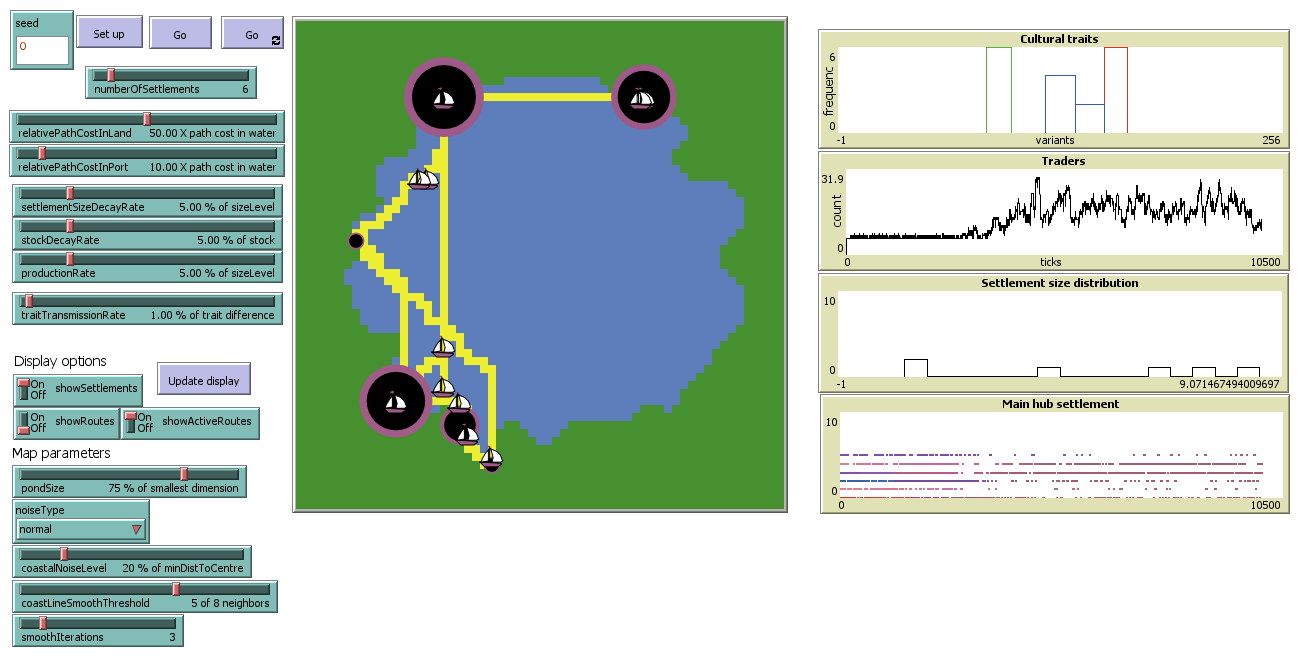
Pond Trade step 10
20.4 Converting parameters into functional agent traits
According to our initial conceptual model, the logical next step would be to implement a mechanism for undirected variation. We can easily include this by adding noise to each trait’s value at each time step. As with transmission, we could regulate it by a global parameter for trait mutation rate. However, we may already have too many global parameters, which we can easily conceive as varying widely across settlements. Thus, we break our plan once again to explore an idea emerging during implementation, like when we defined frequencyOverQuality: what if most of the parameters regulating settlement and trader properties were implemented as traits at the settlement level, recorded in culturalVector, and allowed to evolve? 🤯 Doing this would enable us to represent a more realistic diversity among settlements (i.e. traditions), as well as explore the implications of cultural transmission in trade when traits are not neutral. Will any kind of selection process be observable?
To internalise most parameters as trait values in culturalVector, we must convert all former parameters into hyperparameters, i.e. those values that will be used only to set a range of variation of the settlement-specific values.
| before (step 10) | after (step 11) |
|---|---|
| settlementSizeDecayRate | maxSettlementSizeDecayRate |
| stockDecayRate | maxStockDecayRate |
| productionRate | maxProductionRate |
| traitTransmissionRate | maxTraitTransmissionRate |
| (traitMutationRate) | maxMutationVariation |
We will also further exploit this opportunity and create two additional elements, which we will refer to as land and port technology, to modify how pathCost affects traders’ decisions and movements. For these, we need to introduce two extra hyperparameters, landTechVariation and portTechVariation. Notice that we could do the same for the path cost in water, though it would affect the model’s rhythm more drastically.
20.5 Implementing new settlement traits 🤔
Our goal here will be to implement the following:
- Create all new hyperparameters in the interface
- Create all new traits in
culturalVector
- Implement the new traits in the model logic
- Visualise the new traits using histograms
Before looking at the solution, could you try to write the code yourself?
Things to consider:
- Knowing how to implement the previous cultural vector, how would you implement the new traits?
- How to use the new traits in the model logic?
Solution:
We change the code for initialising settlements so that each trait within culturalVector is sampled randomly according to the hyperparameters above:
to create-coastal-settlements
; consider only coastal patches
let coastalPatches patches with [(isLand = true) and (any? neighbors with [isLand = false])]
repeat numberOfSettlements
[
; ask a random coastal patch without a settlement already
ask one-of coastalPatches with [not any? settlements-here]
[
sprout-settlements 1 ; creates one "turtle" of breed settlements
[
set sizeLevel 1 ; the size level is initiated at minimum (i.e., 1)
set stock 0
set culturalVector extract-rgb color ; 0#, 1# and 2#
; We add seven continuos cultural traits to the neutral RGB traits,
; representing their attitude and ability involving
; aspects we previously fixed as parameters and one variable:
; 3# relativePathCostInLand (normal distribution around global parameter)
set culturalVector lput (random-normal 0 landTechVariation) culturalVector
; 4# relativePathCostInPort (normal distribution around global parameter)
set culturalVector lput (random-normal 0 portTechVariation) culturalVector
; 5# settlementSizeDecayRate [0 - maxSettlementSizeDecayRate)
set culturalVector lput (random-float maxSettlementSizeDecayRate) culturalVector
; 6# stockDecayRate [0 - maxStockDecayRate)
set culturalVector lput (random-float maxStockDecayRate) culturalVector
; 7# produtionRate [0 - maxProductionRate)
set culturalVector lput (random-float maxProductionRate) culturalVector
; 8# frequencyOverQuality [0 - 1)
set culturalVector lput (random-float 1) culturalVector
; 9# traitTransmissionRate [0 - maxTraitTransmissionRate) *** now, it means specifically the 'openess' of a settlement towards other variants of a trait
set culturalVector lput (random-float maxTraitTransmissionRate) culturalVector
; 10# mutationVariation [0 - maxMutationVariation)
set culturalVector lput (random-float maxMutationVariation) culturalVector
set shape "circle 2"
]
; replace the land path cost with the port pathCost
set pathCost relativePathCostInPort
; exclude this patch from the pool of coastal patches
set coastalPatches other coastalPatches
]
]
endAnd then replace the former parameters with the corresponding indexed values in culturalVector:
to update-settlements
ask settlements
[
let thisSettlement self
; the sizeLevel of settlements decays with a constant rate, up to 1 (minimum)
set sizeLevel max (list 1 (sizeLevel * (1 - ((item 5 culturalVector) / 100)) ) )
; production in stock also decays with a constant rate
set stock stock * (1 - ((item 6 culturalVector) / 100))
; prodution is generated in proportion to sizeLevel, following a constant rate
set stock stock + sizeLevel * ((item 7 culturalVector) / 100)
; determine the current and potential number of traders
set currentNumberOfTraders get-current-number-of-traders
set potentialNumberOfTraders get-potential-number-of-traders
; conditions favors the creation of new traders
if (random-float 1 > currentNumberOfTraders / potentialNumberOfTraders )
[
; create a new trader or activate an old one
repeat 1
[
ifelse (any? traders with [not isActivated])
[
ask one-of traders with [not isActivated]
[
setup-trader thisSettlement
move-to thisSettlement
]
]
[
hatch-traders 1
[
setup-trader thisSettlement
]
]
]
set currentNumberOfTraders get-current-number-of-traders ; update currentNumberOfTraders
]
; add variation to the settlement traits (mutation)
mutate-traits
]
end
...
to add-trade-effect [ aTrader ] ; ego = settlement
; cultural transmission trader to port
let newCulturalVector []
foreach culturalVector
[ ?1 ->
let otherSettlementTrait item (length newCulturalVector) [culturalSample] of aTrader
let traitChange (otherSettlementTrait - ?1) * ((item 9 culturalVector) / 100)
set newCulturalVector lput (?1 + traitChange) newCulturalVector
]
; print (word "========== " self " ============")
; print (word "old vector: " culturalVector ", new vector: " newCulturalVector)
set culturalVector newCulturalVector
set sizeLevel sizeLevel + [cargoValue] of aTrader
end
...
to-report get-potential-number-of-traders ; ego = settlement
report (
1 +
(sizeLevel - 1) * (item 8 culturalVector)
)
end
...
to-report get-path-cost [ aPatch aTrader ]
let pathCostOfPatch [pathCost] of aPatch
if ([isLand] of aPatch)
[
ifelse ([any? settlements-here] of aPatch)
[
; path cost in port apply
set pathCostOfPatch pathCostOfPatch + [(item 4 culturalVector)] of [base] of aTrader
]
[
; path cost in land apply
set pathCostOfPatch pathCostOfPatch + [(item 3 culturalVector)] of [base] of aTrader
]
]
report pathCostOfPatch
end20.6 Implementing undirected variation 🤔
To have proper cultural evolution, we need to include another mechanism that modifies cultural vectors randomly through time (undirected variation).
Our goal here will be to implement the following:
- A mechanism that adds random variation to the cultural traits of settlements at each time step
Things to consider:
- How to implement random variation? What probability distribution should we use?
- How to implement the variation mechanism?
- Do these traits need to be bound to a specific range?
Solution:
We add a new procedure that applies random (normally-distributed) mutations to all traits separately and call it in the update-settlements procedure:
to update-settlements
ask settlements
[
let thisSettlement self
...
; add variation to the settlement traits (mutation)
mutate-traits
]
end
...
to mutate-traits
let mutationVariationToApply (item 10 culturalVector) / 100
;print "========================================"
;print culturalVector
; #1, #2 and #3
set culturalVector replace-item 0 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 0 culturalVector) 0 255 mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 1 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 1 culturalVector) 0 255 mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 2 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 2 culturalVector) 0 255 mutationVariationToApply
; #3 and #4 (relativePathCostInLand, relativePathCostInPort)
set culturalVector replace-item 3 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 3 culturalVector) (-1 * relativePathCostInLand + 1) 100 mutationVariationToApply ; arbitrary maximum
set culturalVector replace-item 4 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 4 culturalVector) (-1 * relativePathCostInPort + 1) 100 mutationVariationToApply ; arbitrary maximum
; #5, #6 and #6 (settlementSizeDecayRate, stockDecayRate, produtionRate)
set culturalVector replace-item 5 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 5 culturalVector) 0 maxSettlementSizeDecayRate mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 6 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 6 culturalVector) 0 maxStockDecayRate mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 7 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 7 culturalVector) 0 maxProductionRate mutationVariationToApply
; #8, #9 and #10 (frequencyOverQuality, traitTransmissionRate, mutationVariation)
set culturalVector replace-item 8 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 8 culturalVector) 0 1 mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 9 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 9 culturalVector) 0 maxTraitTransmissionRate mutationVariationToApply
set culturalVector replace-item 10 culturalVector mutate-trait (item 10 culturalVector) 0 maxMutationVariation mutationVariationToApply
;print culturalVector
end
to-report mutate-trait [ traitValue minValue maxValue mutationVar ]
report (max (list minValue min (list maxValue (traitValue + (random-normal 0 mutationVar) * (maxValue - minValue)))))
endTo better visualise the distribution of traits along with the simulation, we add four new Plots to our interface. These are histograms of the values for each trait and settlement, giving us a sense of both convergence (or cultural integration) and possibly revealing evolutionary trends driven by trait selection. For instance, we would expect high selective pressure on settlements with higher production rates, since they are part of the positive feedback loops we implemented earlier in the first tier.
20.7 Adding a stop condition
At this stage, we also had to introduce stop conditions to interrupt simulation runs, especially given the potential number of traders under some parameter configurations. The conditions are added to the go procedure:
to go
tick
if (ticks = 10000 or count turtles > 500) [ stop ]
update-traders
update-settlements
update-display
end20.8 Checking the milestone File (step 11)
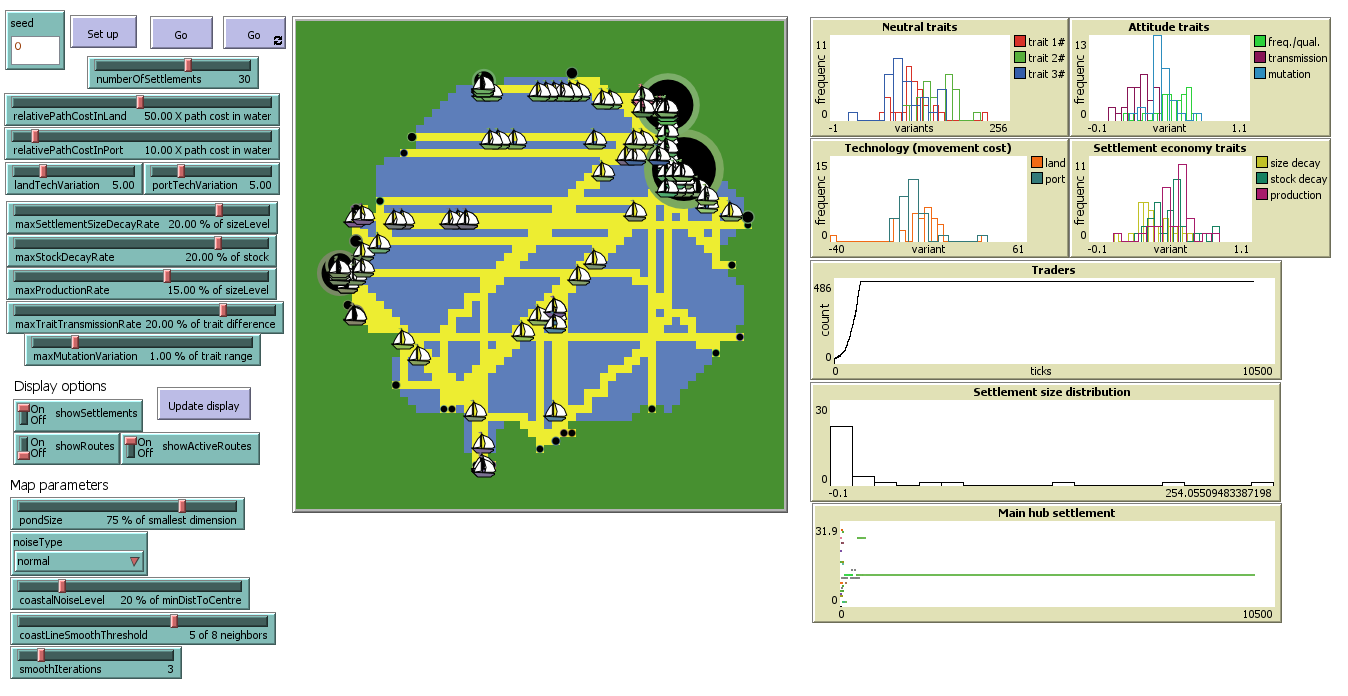
Pond Trade step 11